Mathematics
Mathematics includes the study of such topics as quantity (number theory), structure (algebra), space (geometry), and change (mathematical analysis). It has no generally accepted definition.
- https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matem%C3%A1ticas
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematics#cite_note-Mura-7
- Number theory (or arithmetic)
- Linear algebra https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_algebra
- Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations, linear maps, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrices.
- Mathematical analysis (Math of change) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_analysis
- Analytic geometry https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytic_geometry
- Infinitesimal calculus (Math of change) (The study of things that change) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calculus
- Differential calculus (Derivative) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differential_calculus
- Integral calculus https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integral
- Fundamental theorem of calculus https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fundamental_theorem_of_calculus
- One of the applications of Mathematical analysis (Calculus in particular) is for Signal processing
- Applied mathematics: Some disciplines are considered to be applied mathematics. Sin embargo, no me queda claro si las área que estoy enumerando aquí realmente forman parte de lo que se conoce como Applied mathematics. En particular, Statistics can be considered to be a distinct mathematical science rather than a branch of mathematics. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistics
- Discrete mathematics https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_mathematics
- Numerical analysis https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Numerical_analysis
- Computer algebra https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_algebra
- Statistics https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistics
- Applications of mathematics:
-
- One of the applications of Mathematical analysis (Calculus in particular) is for Signal processing.
Numbers
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real_number
- Real numbers (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{R}} ) include the rational numbers (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{Q}} ), which include the integers (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{Z}} ), which in turn include the natural numbers (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{N}} )
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{R}} : A real number is a value of a continuous quantity that can represent a distance along a line (or alternatively, a quantity that can be represented as an infinite decimal expansion). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real_number
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{Q}} : A rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p/q} of two integers, a numerator Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} , and a non-zero denominator Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} . https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rational_number
- Numbers like Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{2}} or Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers, but can be represented on real number line. https://socratic.org/questions/what-is-the-difference-between-real-numbers-and-rational-numbers
What is a function
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Function_(mathematics)
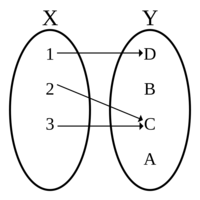
Diagram of a function, with domain Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X = {1, 2, 3}}
and codomain Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y = {A, B, C, D}}
, which is defined by the set of ordered pairs Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {(1, D), (2, C), (3, C)}}
. The image/range is the set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {C, D}}
. Taken from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Function_(mathematics)
<htmltag tagname="img" src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/64/Codomain2.SVG">
</htmltag>

A function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f}
from Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X}
to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y}
. The blue oval Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y}
is the codomain of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f}
. The yellow oval inside Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y}
is the image of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f}
. The term range is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or image of a function. Taken from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Codomain
- In mathematics, a function is a binary relation over two sets that associates every element of the first set, to exactly one element of the second set.
- Intuitively, a function is a process that associates each element of a set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} , to a single element of a set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} .
- Formally, a function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f} from a set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} to a set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} is defined by a set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G} of ordered pairs Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x, y)} such that Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x \in X} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y \in Y} .
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} are resctively called the domain and the codomain of the function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f} . The term range is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or image of a function [See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Codomain]
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G} is called the graph of the function. In mathematics, the graph of a function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f} is the set of ordered pairs Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x, y)} , where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = y} .
- In mathematically we usually write Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = f(x)}
- We say Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} is a function of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x}
- Which means that mathematically Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} depends on Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} .
- So, as in this case, the independent variable is often designated by Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} . The dependent variable is often designated by Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} .
- A basic example of a function: Linear Functions: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_function
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = ax + b}
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = ax + b}
- Where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b} are constants. Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} is frequently referred to as the slope of the line, and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b} as the intercept.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \in} ℝ
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = -x + 5}
|
Continuity
- A rigorous definition of continuity of real functions is usually given in a first course in calculus in terms of the idea of a limit. First, a function f with variable x is said to be continuous at the point c on the real line, if the limit of f(x), as x approaches that point c, is equal to the value f(c); and second, the function (as a whole) is said to be continuous, if it is continuous at every point. A function is said to be discontinuous (or to have a discontinuity) at some point when it is not continuous there. These points themselves are also addressed as discontinuities. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continuous_function

- A sequence of continuous functions fn(x) whose (pointwise) limit function f(x) is discontinuous. The convergence is not uniform. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continuous_function
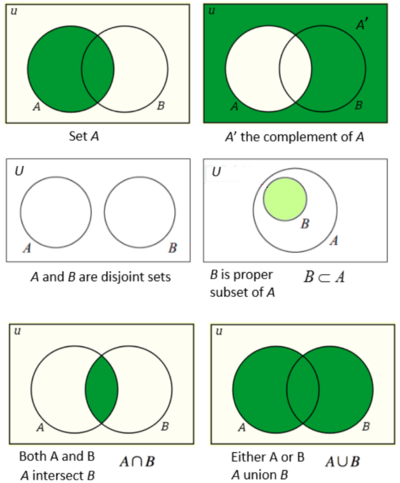
Union - Intersection - Complement
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/math4libarts/chapter/union-intersection-and-complement