Difference between revisions of "Big Data Integration"
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 401: | Line 401: | ||
[[File:Rails_sey_hello2.png|400px|thumb|center|]] | [[File:Rails_sey_hello2.png|400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Notice that if you hit Refresh in your browse, the time updates each time the page is displayed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Adding the time===== | ||
| + | Our original problem was to display the time to users of our application. We now know how to make our application display dynamic data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second issue we have to address is working out where to get the time from. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We've shown that the approach of embedding a call to Ruby's ''Time.now()'' method in our ''hello.html.erb'' template works. Each time we access this page, the user will see the current time substituted into the body of the response. And for our trivial application, that might be good enough. In general, though, we probably want to do something slightly different. We'll move the determination of the time to be displayed into the controller and leave the view with the simple job of displaying it. We'll change our action method in the controller to set the time value into an instance variable called @time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | app/controllers/say_controller.rb | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
| + | class SayController < ApplicationController | ||
| + | def hello | ||
| + | @time = Time.now | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | def goodbye | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the ''.html.erb'' template, we'll use this instance variable to substitute the time into the output: | ||
| + | app/views/say/hello.html.erb | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="html"> | ||
| + | <h1>Hello from Rails!</h1> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | It is now <%= @time %> | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | When we refresh our browser, we eill again see the current time, '''showing that the communication between the controller and the view was succesfull.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Why did we go to the extra trouble of setting the time to be displayed in the controller and then using it in the view? Good question. In this application it donen't make much difference, but by putting the logic in the controller instead, we buy ourselves some benefits. For example, we may want to extend our application in the future to support users in many countries. In tat case, we'd want to localize the display of the time, choosing a tie appropriate to their time zone. That would be a fair amount of application-level code, and it would probably not be appropriate to embed it at the view level. By setting the time to display in the controller, we make our application more flexible, we can change the time zone in the controller without having to update any view that uses the time object. The time is data, and is should be supplied to the view by controller. We'll see a lot more of this whewn we introduce models into the equation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====The story so far===== | ||
| + | Let's briefly review how oru current application works. | ||
| + | * The user navigates to our application. In our case, we do that useing a local URL such as http://localhost:3000/say/hello | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Rails then matches the route pattern, which it previously split into two parts and analyzed. | ||
| + | : The ''say'' part is taken to be the name of a controller, so Rails creates a new instance of the Ruby class ''SayController' (which it finds in ''app/controllers/say_controller.rb). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The next part of the pattern, ''hello', identifies an action. Rails invokes a method of that name in the controller. This action method creates a new ''time'' object holding the current time and tuchs it away in the ''@time'' instance variable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Rails looks for a template to display the result. It searches the directory ''app/views'' for a subdirectory with the same name as the controller (''say'') and in that subdirectory for a file named after the action (''hello.html.erb''). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Rails processes this file through the ERB templating system, executing and embedded Ruby and substituting in vaues set up by the controller. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The result is returned to the browser, and Rails finches processing this request. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =====Linking pages together===== | ||
| + | Normally, each page in your application will correspond to a separate view. In our case, we''ll also use a new action method to handle the page (although that isn't always the case, as we'll see later in the book). We'll use the same controller for both actions. Again, this needn't be the case, but we have no compelling reason to use a new controller right now. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We already defined a '''''goodbye''''' action for this controller, so all that remains is to create a new template in the directory ''app/views/say''. This time it's called ''goodbye.html.erb'' because by default templates are named after their associated actions: | ||
| + | |||
| + | app/views/say/goodbye.html.erb | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="html"> | ||
| + | <h1>Goodbye!</h1> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | It was nice having you here. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://localhost:3000/say/goodbye | ||
Revision as of 13:58, 9 March 2019
Contents
Module Information
Module Objectives
- How to implement a cloud based storage solution for a company's big data needs
- The knowledge needed to integrate desktop and web applications to utilize web services and stored data.
- How cloud based DNS solutions can help to optimize a company's IT infrastructure
- How cloud based servers and service implementations can be easily deployed for rapid utilisation
- The steps involved in data exchange between web services and cloud based applications
Resources - References
- Programming Amazon EC2, Juirg van Vliet 1st 2011 O’Reilly
- Google Compute Engine, Marc Cohen 1st 2011 O’Reilly
- Python for Google App Engine, Massimiliano Pippi 1st 2015 Packet
- Big Data Fundamentals Concepts, Drivers & Techniques, Thomas Erl, Wajid Khattak, and Paul Buhler, Prentice Hall
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- A service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a style of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network.
- A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online.
- SOA provides access to reusable Web services over a TCP/IP network,
XML
Web service
- A software component stored on one computer that can be accessed via method calls by an application (or other software component) on another computer over a network
- Web services communicate using such technologies as:
- XML, JSON and HTTP
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP): An XML-based protocol that allows web services and clients to communicate in a platform-independent manner
Basic concepts:
- Remote machine or server: The computer on which a web service resides
- A client application that accesses a web service sends a method call over a network to the remote machine, which processes the call and returns a response over the network to the application
- Publishing (deploying) a web service: Making a web service available to receive client requests.
- Consuming a web service: Using a web service from a client application.
- In Java, a web service is implemented as a class that resides on a server.
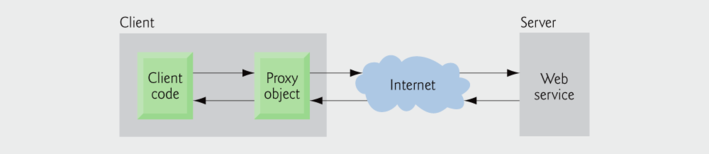
An application that consumes a web service (client) needs:
- An object of a proxy class for interacting with the web service.
- The proxy object handles the details of communicating with the web service on the client's behalf
JAX-WS:
- The Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS) is a Java programming language API for creating web services, particularly SOAP services. JAX-WS is one of the Java XML programming APIs. It is part of the Java EE platform.
- Requests to and responses from web services are typically transmitted via SOAP.
- Any client capable of generating and processing SOAP messages can interact with a web service, regardless of the language in which the web service is written.
Creating - Deploying - Testing and Describing a Web Service using NetBeans
- In Netbeans, you focus on the logic of the web service and let the IDE handle the web service’s infrastructure
- We first need to to do some configuration in NetBeans:
- Go to /usr/local/netbeans-8.2/etc/netbeans.conf:
- Find the line: netbeans_default_options
- If -J-Djavax.xml.accessExternalSchema=all is not between the quotes then paste it in.
- Go to /usr/local/netbeans-8.2/etc/netbeans.conf:
- If you are deploying to the GlassFish Server you need to modify the configuration file of the GlassFish Server (domain.xml):
- /usr/local/glassfish-4.1.1/glassfish/domains/domain1/config/domain.xml
- Find : <java-config
- Check the jvm-options for the following configuration: <jvm-options>-Djavax.xml.accessExternalSchema=all</jvm-options>
- It should be there by default, if not paste it in, save file and exit
- You can now start Netbeans IDE
- /usr/local/glassfish-4.1.1/glassfish/domains/domain1/config/domain.xml
- Create a Web Service in NetBeans- Locally
- Choose File > New Project:
- Select Web Application from the Java Web category
- Change Project Name: to CalculatorWSApplication
- Set the server to GlassFish 4.1.1
- Set Java EE Version: Java EE 7 Web
- Set Context path: /CalculatorWSApplication
- After that you should now have a project created in the Projects view on the left hand side.
- Creating a WS from a Java Class:
- Right-click the CalculatorWSApplication node and choose New > Web Service.
- If the option is not there choose Other > Web Services > Web Service
- Click Next
- Name the web service CalculatorWS and type com.hduser.calculator in Package. Leave Create Web Service from Scratch selected.
- Select Implement Web Service as a Stateless Session Bean.
- Click Finish. The Projects window displays the structure of the new web service and the source code is shown in the editor area. A default hello web service is created by Netbeans.
- Adding an Operation to the WS:
- Change to the Design view in the editor.
- Click the Add operation button.
- In the upper part of the Add Operation dialog box, type add in Name and type int' in the Return Type drop-down list.
- In the lower part of the Add Operation dialog box, click Add and create a parameter of type int named num_1.
- Click Add again and create a parameter of type int called num_2.
- Click OK at the bottom of the panel to add the operation.
- Remove the default hello operation: Right click on hello operation and choose: Remove Operation
- Click on the source view to go back to view the code in the editor.
- You will see the default hello code is gone and the new add method is now there instead.
- Now we have to alter the code to look like this.
/* * To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties. * To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates * and open the template in the editor. */ package com.adelo.calculator; import javax.jws.WebService; import javax.jws.WebMethod; import javax.jws.WebParam; import javax.ejb.Stateless; @WebService(serviceName = "CalculatorWS") @Stateless() public class CalculatorWS { /** * Web service operation */ @WebMethod(operationName = "add") public int add(@WebParam(name = "num_1") int num_1, @WebParam(name = "num_2") int num_2) { //TODO write your implementation code here: int result = num_1 + num_2; return result; } }
- Well done, you have just created your first Web Service.
- To test the Web service drop down the Web Services directory and right click on CalculatorWSApplication.
- Choose Test Web service.
- Netbeans throws an error: It is letting us know that we have not deployed our Web Service.
- Right click on the main Project node and select deploy
- Testing the WS:
- Deploying the Web Service will automatically start the GlassFish server. Allow the server to start, this will take a little while. You can check the progress by clicking on the GlassFish tab at the bottom of the IDE.
- Wait until you see: «CalculatorWSApplication was successfully deployed in 9,912 milliseconds»
- Now you can right click on the Web Service as before and choose Test Web Service.
- The browser will open and you can now test the Web service and view the WSDL file.
- You can also view the Soap Request and Response.
Consuming the Web Service
From a Web Application project
- Now that we have a web service we need a client to consume it.
- Choose File > New Project
- Select Web Application from the Java Web category
- Name the project CalculatorWSJSPClient
- Leave the server and java version as before and click Finish.
- Expand the Web Pages node under the project node and delete index.html.
- Right-click the Web Pages node and choose New > JSP in the popup menu.
- If JSP is not available in the popup menu, choose New > Other and select JSP in the Web category of the New File wizard.
- Type index for the name of the JSP file in the New File wizard. Click Finish to create the JSP (Java Server Page)
- Right-click the CalculatorWSJSPClient node and choose New > Web Service Client.
- If the option is not there choose Other > Web Services > Web Service Client
- Select Project as the WSDL source. Click Browse. Browse to the CalculatorWS web service in the CalculatorWSApplication project. When you have selected the web service, click OK.
- Do not select a package name. Leave this field empty.
- Leave the other settings as default and click Finish.
- The WSDL gets parsed and generates the .java
- The Web Service References directory now contains the add method we created in our web service.
- Drag and drop the add method just below the H1 tags in index.jsp
- The Code will be automatically generated.
- Change the values of num_1 and num_2 to any two numbers e.g. 5 and 5 as per test earlier.
- Remove the TODO line from the catch block of the code and paste in:
- out.println("exception" + ex);
- If there is an error this will help us identify the problem.
- IMPORTANT Once you close Netbeans you are shutting down your server. If you want to reuse a Web Service you must re-deploy.
- Consuming Live WS:
- Again we are going to need a client.
- File > New Project > Java Web > Web Application.
- This time name it SortClient.
- Click Next
- Leave the Server and Java Version settings as before (should be default now)
- Context path : /SortClient
- Click Finish
From a Java project
Netbeans 6.5 - 9 and Java EE enable programmers to "publish (deploy)" and/or "consume (client request)" web services
This document provides step-by-step instructions to consume a web service in Java using NetBeans IDE.
In the project, we will invoke a sorting web service through its WSDL link: http://vhost3.cs.rit.edu/SortServ/Service.svc?singleWsdl
- Step 1 - Createa JavaProject:
- We are going to name it: SortClient
- Step 2 - Generate a Web Service Client:
- After the Java Project has been created, go to the Project Tree Structure, Right click on Project and select New and then choose Web Service Client.
- Specify the WSDL URL as: http://vhost3.cs.rit.edu/SortServ/Service.svc?singleWsdl
- Click Finish
- Step 3 - Invoke the Service:
- Expand the Web Service References until you see the operation lists. Drag the operation you want to invoke to the source code window, such as "GetKey". A piece of code is automatically generated to invoke that operation.
- Drag MergeSort to the source code window and the corresponding code is automatically generated,too.
- In the main function, add the code to call the two functions: getKey() and mergeSort();As it is a call to a remote service, RemoteException needs to be listed in the throws cause
Rails
https://guides.rubyonrails.org/getting_started.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ruby_on_Rails
Ruby on Rails, or Rails, is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model-view-controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and web pages. It encourages and facilitates the use of web standards such as JSON or XML for data transfer, HTML, CSS and JavaScript for user interfacing.
Installation
Ruby installation:
sudo apt install ruby
Rails installation:
sudo apt install ruby-railties
sudo apt-get install rails
For gem installation:
sudo apt-get install gem
sudo apt-get install nodejs
sudo gem install bundler
How to create a Rails Application
When you install the Rails framework, you also get a new command-line tool, rails, that is used to construct each new Rails application you write.
Why do we need a tool? Why can't we just hack away in our favorite editor and create the source for our application from scratch? Well, we could just hack; after all, a Rails application is just Ruby source code. But Rails also does a lot of magic behind the curtain to get our application to work with a minumum of explicit configuration. To get this magic to work, Rails needs to find all the various componenets of your application. Aas we'll see later, this means we need to create a specific directory structure, slotting the code we write into the appropriate places. The rails command simply creates this directory structure for us and populates it with some standards Rails code.
To create your first Rails application:
rails new myrailsapp
The above command has created a directory named myrailsapp.
Examine your installation using the following command:
rake about
Once you get rake about working, you have everything you need to start a standar-alone web server that can run our newly created Rails application. So, let's star our demos application:
rails server Rails 4.2.10 application starting in development on http://localhost:3000
At this point, we have a new application running, but it has none of our code in it.
Hello Rails
Let's start by creating a "Hello, world!"
Rails is a Model-View-Controller framework. Rails accepts incoming request from a browser, decodes the request to find a controller, and calls an action method in that controller. The controller then invokes a particular view to display the results to the user. To write our simple "Hello World!" application, we need code for a controller and a view, and we need a route to connect the two. We don't need code for a model, because we're not dealing with any data. Let's start with the controller.
In the same way that we used the rails commands to create a new Rails application, we can also use a generator script to create a new controller for our project. This command is called rails generate . So, to create a controller called say, we run the command passing in the name of the controller we want to create and the names of the actions we intend for this controller to support:
rails generate controller Say hello goodbye
create app/controllers/say_controller.rb
route get 'say/goodbye'
route get 'say/hello'
invoke erb
create app/views/say
create app/views/say/hello.html.erb
create app/views/say/goodbye.html.erb
invoke test_unit
create test/controllers/say_controller_test.rb
invoke helper
create app/helpers/say_helper.rb
invoke test_unit
invoke assets
invoke coffee
create app/assets/javascripts/say.coffee
invoke scss
create app/assets/stylesheets/say.scss
Notice the files that were generated for the rails generate command. The first source file we'll be looking at is the controller:
app/controllers/say_controller.rb
class SayController < ApplicationController
def hello
end
def goodbye
end
end
SayController is a class that inherits from ApplicationController, so it automatically gets all the default controller behavior. What does this code have to do? For now, it does nothing, we sinply have empty action methods named hello() and goodbye(). To understand why these methods are named this way, we need to look at the way Rails handles requests.
Rails and Request URLs
Like any other web application, a Rails application appears to its users to be associated with a URL. When you point your browser at that URL, you are talking to the application code, which generates a respondse to you.
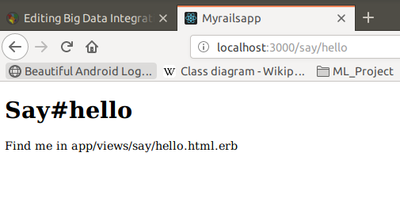
Let's try it now. Navigate to the URL http://localhost:3000/say/hello
You'll see something that looks like this:
Our first action
At this point, we can see not only that we have connected the URL to our controller but also tat Rails is pointing the way to our next step, namely, to tell Rails what to display. That's where views come in. Remember when we ran the script to create the new controller? That command added several files and a new directory to our application. That directory contains the template files to the controller's view. In our case, we created a controller named say, so the view will be in the directory app/views/say.
By default, Rails looks for templates in a file with the same name as the action it's handling. In our case, that means we need to replace a file called hello.html.erb in the directory app/views/say. (Why .html.erb? We'll explain in a minute.) For now, let's just put some basic HTML in there:
app/views/say/hello.html.erb
<h1>Hello from Rails!</h1>
Save the file hello.html.erb and refresh your browser.
In total, we've looked at two files in our Rails application tree. We looked at the controller, and we modified a template to display a page in the browser.
These files live in standard locations in the Rails hierarchy: controllers go into app/controllers, and views go into sub-directories of app/views:
.
├── app
│ ├── assets
│ │ ├── images
│ │ ├── javascripts
│ │ │ ├── application.js
│ │ │ └── say.coffee
│ │ └── stylesheets
│ │ ├── application.css
│ │ └── say.scss
│ ├── controllers
│ │ ├── application_controller.rb
│ │ ├── concerns
│ │ └── 'say_controller.rb'
│ ├── helpers
│ │ ├── application_helper.rb
│ │ └── say_helper.rb
│ ├── mailers
│ ├── models
│ │ └── concerns
│ └── views
│ ├── layouts
│ │ └── application.html.erb
│ └── say
│ ├── goodbye.html.erb
│ └── 'hello.html.erb'
├── bin
│ ├── bundle
│ ├── rails
│ ├── rake
.
.
.
Making it dynamic
So far, our Rails application is pretty boring, it just displays a static page. To make it more dynamic, let's have it show the current time each time it displays the page.
To do this, we need to change the template file in the view, it now needs to include the time as a string. That raises two questions. First, how do we add dynamic content to a template? Second, where do we get the time from?
=Dynamic content
There are many ways of creating dynamic templates in Rails. The most common way, which we'll use here, is to embed Ruby code in the template. That's why we nemed our template file hello.html.erb; the '.html.erb suffix tells Rails to expand the content in the file using a system called ERB.
ERB is a filter that is installed as part of the Rails installation that takes an .erbfile and outputs a tranformed version. The output file is often HTML in Rails, but it can be anyting. Normal content is passed through without being changed. However, content between <%= and %> is interpreted as Ruby code and executed. The result of that exwcution is converted into a string, and that value is subtituted in the file in place of the <%=...%> sequence. For example, chage hello.html.erb to display the current time:
app/views/say/hello.html.erb
<h1>Hello from Rails!</h1>
<p>
It is now <%= Time.now %>
</p>
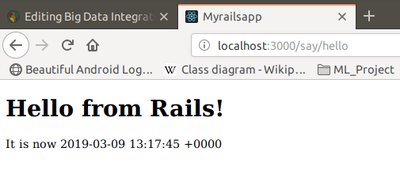
Notice that if you hit Refresh in your browse, the time updates each time the page is displayed.
Adding the time
Our original problem was to display the time to users of our application. We now know how to make our application display dynamic data.
The second issue we have to address is working out where to get the time from.
We've shown that the approach of embedding a call to Ruby's Time.now() method in our hello.html.erb template works. Each time we access this page, the user will see the current time substituted into the body of the response. And for our trivial application, that might be good enough. In general, though, we probably want to do something slightly different. We'll move the determination of the time to be displayed into the controller and leave the view with the simple job of displaying it. We'll change our action method in the controller to set the time value into an instance variable called @time.
app/controllers/say_controller.rb
class SayController < ApplicationController
def hello
@time = Time.now
end
def goodbye
end
end
In the .html.erb template, we'll use this instance variable to substitute the time into the output:
app/views/say/hello.html.erb
<h1>Hello from Rails!</h1>
<p>
It is now <%= @time %>
</p>
When we refresh our browser, we eill again see the current time, showing that the communication between the controller and the view was succesfull.
Why did we go to the extra trouble of setting the time to be displayed in the controller and then using it in the view? Good question. In this application it donen't make much difference, but by putting the logic in the controller instead, we buy ourselves some benefits. For example, we may want to extend our application in the future to support users in many countries. In tat case, we'd want to localize the display of the time, choosing a tie appropriate to their time zone. That would be a fair amount of application-level code, and it would probably not be appropriate to embed it at the view level. By setting the time to display in the controller, we make our application more flexible, we can change the time zone in the controller without having to update any view that uses the time object. The time is data, and is should be supplied to the view by controller. We'll see a lot more of this whewn we introduce models into the equation.
The story so far
Let's briefly review how oru current application works.
- The user navigates to our application. In our case, we do that useing a local URL such as http://localhost:3000/say/hello
- Rails then matches the route pattern, which it previously split into two parts and analyzed.
- The say part is taken to be the name of a controller, so Rails creates a new instance of the Ruby class SayController' (which it finds in app/controllers/say_controller.rb).
- The next part of the pattern, hello', identifies an action. Rails invokes a method of that name in the controller. This action method creates a new time object holding the current time and tuchs it away in the @time instance variable.
- Rails looks for a template to display the result. It searches the directory app/views for a subdirectory with the same name as the controller (say) and in that subdirectory for a file named after the action (hello.html.erb).
- Rails processes this file through the ERB templating system, executing and embedded Ruby and substituting in vaues set up by the controller.
- The result is returned to the browser, and Rails finches processing this request.
Linking pages together
Normally, each page in your application will correspond to a separate view. In our case, well also use a new action method to handle the page (although that isn't always the case, as we'll see later in the book). We'll use the same controller for both actions. Again, this needn't be the case, but we have no compelling reason to use a new controller right now.
We already defined a goodbye action for this controller, so all that remains is to create a new template in the directory app/views/say. This time it's called goodbye.html.erb because by default templates are named after their associated actions:
app/views/say/goodbye.html.erb
<h1>Goodbye!</h1>
<p>
It was nice having you here.
</p>